Transmission in the United States: What Makes Developing Electric Transmission So Hard?
White Paper
Let’s Work Together
We don’t solve problems with canned methodologies; we help you solve the right problem in the right way. Our experience ensures that the solution works for you.
Related Insights

Transmission Implications for Clean Energy Goals
Article
In this report, we discuss several challenges to transmission development in detail, and we offer a few examples of successes and potential paths forward.

Massachusetts Releases Roadmap to Achieve Net-Zero Emissions by 2050
Article
While this roadmap is specific to Massachusetts, as an early mover in developing various pathways and sector analysis, the Commonwealth’s approach may provide a framework for other…

COVID-19 Response – What You Should be Thinking About: Regulatory Strategy and Cost Recovery
Article
Developing a regulatory plan now will enable utilities to more efficiently manage the recovery period of COVID-19. Learn about what commissions and utility leaders should be considering.

FERC Announced Notice of Proposed Rulemaking
Article
When implemented, the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978 (PURPA) set off a multi-decade period of competitive transition for electricity markets. This article highlights how FERC…

Informing the Transmission Discussion
Article
This report, prepared by ScottMadden for WIRES, includes a comprehensive overview of the state of play of transmission. It examines, region by region, the challenges posed by…

Prioritizing Transmission and Distribution Investments
White Paper
There is often an insightful story hidden in the data which will tells you how you are operating the business, and the objective of data analysis is…

Transmission Development – Key Issues to Watch
Report
ScottMadden’s Cristin Lyons joined SNL in 2013 to provide an interactive webinar focused on transmission development.

Top Considerations for Leaders When Electrifying Utility Fleets
Article
As owners and operators of vehicle fleets as well as providers of electricity, utilities have a unique opportunity to take advantage of fleet electrification. Through their own…

Four Steps to Building a Successful Electric Vehicle Make-Ready Program
Article
As decarbonization efforts have proliferated, electric vehicles (EVs) are widely seen as essential to meeting state and local clean energy goals. However, in order to meet the…

Building It Together: An Ecosystem Approach to Fleet Electrification
Article
Electrifying vehicle fleets will present both challenges and opportunities for electric utilities. Due to the potentially large, concentrated, and variable loads, it is critical that utilities engage…

The ScottMadden Grid Modernization Road Map
Video
The following video features Cristin Lyons, partner and energy practice leader and Justin Stevens, partner as they discuss the ScottMadden Grid Modernization Road Map – a set…
15 States Sign Joint Commitment to Accelerate the Deployment of Medium- and Heavy-Duty Vehicles
Article
Light-duty consumer vehicles often own the spotlight in the world of electric vehicles. Now, 15 states have put their focus on accelerating the market for electric medium-…

The Nexus of COVID-19 Recovery and ESG Performance
Article
This article highlights how an effective recovery approach to COVID-19 will take a long-term view and addresses the following areas essential to ESG strategy.

Lessons Learned from Hawaii: Bold Visions Require New Paradigms
Article
How does Hawaii plan to achieve its ambitious goal of 100% renewable energy by 2045? This ScottMadden and SEPA article, featured in the April 2020 Public Utilities…

New York Energy Storage Order
White Paper
New York recently issued an Order setting energy targets for the state and establishing policies to drive energy storage development. This white paper explores key topics and…

Four Keys to a Successful Grid Modernization Program
White Paper
Recent headwinds from regulators in some states have shown that the grid modernization proposals of utilities are by no means guaranteed approval. This white paper highlights the…

Opportunities and Benefits of the Western Energy Imbalance Market as Options Continue to Grow
Article
The evolution of energy markets presents financial and operational benefits for participating utilities. Access this ScottMadden article to learn about key considerations for potential market participants.

Shaping a Path Toward High-Renewable Penetration: A Comparison of Utility-Scale and Distributed Renewables
White Paper
Access this white paper for an in-depth comparison of utility-scale and distributed renewables. Learn how to best integrate and effectively manage these resources to maximize benefits to…

Illinois Remains at the Forefront of Grid Modernization Advancements: DERs, Renewables, and Beyond
White Paper
This update profiles continued progress in smart grid investments, reliability achievements under the Energy Infrastructure Modernization Act (EIMA), and the recently completed NextGrid Illinois of the Future…

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 18, Issue 2
Energy Industry Update
Themed "Don’t Stop Believin'," this issue explores the growth strategies energy and utility companies are undertaking and how they are developing and modernizing needed infrastructure. We also…

Energy Industry Update—Don’t Stop Believin’: A Special Edition for the Utility Supply Chain Conference
Report
During the 2019 Utility Supply Chain Conference, Cristin Lyons reviewed the latest Energy Industry Update and shared key highlights for topics including electrification, wholesale energy infrastructure development,…

The Energy Industry Update Webcast: Generation to Generation: An Energy Evolution
Report
This webinar recording reviews bid-based wholesale power markets, the future of utility-scale solar, and grid investment. View this recording to hear from our expert leads.

How will NY REV Impact Energy Storage?
Article
Are you wondering how New York’s Reforming the Energy Vision proceedings will impact the market for energy storage? ScottMadden recently moderated a panel on the role of…

Six Keys for Utilities to Successfully Scale Energy Efficiency Programs
Article
New utility and state carbon-reduction goals, increasingly favorable economics, and incentives to adopt EE all contribute to the need for some utilities to scale their EE programs.…

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 17, Issue 1
Energy Industry Update
The latest Energy Industry Update examines the direction and magnitude of some of the changes and what utilities are doing to prepare for and thrive in a…

Establishing Solar Tariffs in the New Reality of Distributed Generation
Case Study
This case study highlights how ScottMadden was able to successfully assist one of the nation’s largest municipally owned electric utility in updating its solar program.

Impacts of Distributed Energy Resources on T&D Organizations
Article
As a leader of your transmission and distribution (T&D) organization within vertically integrated or “wires-only” utilities, you face sweeping change. Pressing challenges, such as decreasing load, increasing…

State of the Energy Industry: A Mid-Year Review
Report
State of the Energy Industry: A Mid-Year Review (or “I Feel the Earth Move under My Feet” – with apologies to Carole King)

Improving Capital Project Planning and Execution
Case Study
A small privately held transmission and distribution utility located in the Northeast sought to improve its capital project planning and project management capabilities.

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 10, Issue 1
Energy Industry Update
In the January 2010 issue of The ScottMadden Energy Industry Update, we look at areas engaging the industry during these uncertain times—investor views, the generation mix, gas…

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 17, Issue 2
Energy Industry Update
This Update, themed “Generation to Generation: An Energy Evolution,” examines the strategic drivers that are challenging, and propelling, our industry and what utilities are doing to anticipate,…

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 18, Issue 1
Energy Industry Update
Themed “Recalibration,” this Update examines some of the emerging and continuing trends in the industry, with the hope that it will help energy executives “recalibrate” as our…

Infrastructure and Technology – Volume 17 – Issue 1
Report
In this section of the Energy Industry Update, we provide a comparison of grid transformation developments in California and New York and an update on North American…

Infrastructure and Technology – Volume 16 – Issue 2
In this section, we look at the growth in microgrids in the United States and energy reforms in Mexico aimed at boosting investment and improving energy infrastructure.

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 12, Issue 1
Energy Industry Update
The Energy Industry Update – Spring 2012 Managing with Uncertainty Fatigue

The Electricity Business of the Future
Video
At the 2019 Duke University Energy Conference, ScottMadden's Cristin Lyons joined a panel of leading industry experts to discuss the future of the electricity business.

Decarbonization and RIIO in the United Kingdom
Article
During a recent fact-finding trip to the U.K., led by SEPA, we gathered practical lessons for the U.S. and new approaches to growing challenges in the industry.…

Transmission Investment: Revisiting the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s Two-Step DCF Methodology for Calculating Allowed Returns on Equity
White Paper
This white paper, prepared on behalf of the EEI, reviews the “Two-step” Discounted Cash Flow model to set allowed Returns on Equity for electric transmission investments, as…

FERC Order No. 1000: Five Years On
White Paper
This complimentary white paper addresses the objectives of Order No. 1000, what has been accomplished, and key challenges with its implementation.

How Renewables and Distributed Resources Have Impacted Transmission in Germany
Report
ScottMadden recently joined the Solar Electric Power Association to lead a group of U.S. energy industry executives to Germany to exchange information with electricity and solar market…

Confirming Compliance – Do You Have Proper Oversight of Your Contractors?
Report
Establishing a governance model for NERC compliance is key to mitigate violations found by auditors and avoid costly fines for governance models.
The Energy Industry Update – Volume 15, Issue 2
Energy Industry Update
The electric industry seems to be on the cusp of great change. Regulators are rethinking the hundred-year-old rate-of-return paradigm, renewables costs are falling (especially for solar photovoltaic…

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 14, Issue 2
Energy Industry Update
The ScottMadden Energy Industry Update – August 2014 I Feel the Earth Move under My Feet

ScottMadden Supports an Impressive Turnaround at EKPC with Strategic and Business Planning
Case Study
ScottMadden was asked to work with EKPC, a generation and transmission cooperative, to develop a new strategic and business plan for the generation and transmission cooperative.

ScottMadden Insight: Generation Trends – What Are the Impacts on Transmission?
Report
ScottMadden Insight: Supply Trends – What Are the Impacts on Transmission? Infocast’s Transmission Summit West Executive Forum

Start-up of a New Transmission Company
Case Study
An independent transmission company sought to build, own, and operate transmission assets in Texas. ScottMadden was retained to assist with developing the operating strategy for the new control…

Energy Imbalance Market
Report
In this presentation, we will look at the operational considerations for joining the Energy Imbalance Market (EIM) across the following categories: marketing and trading, transmission operations, generation,…

A Survey of the Generation Landscape
Report
During the 2016 Transmission Summit, ScottMadden reviewed the generation landscape and the impacts of the Clean Power Plan.
The Energy Industry Update – Volume 5, Issue 2
Energy Industry Update
The Energy Industry Update (EIU) is a compendium of breaking news, emerging issues, and recent developments in the energy industry.

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 5, Issue 1
Energy Industry Update
The Energy Industry Update (EIU) is a compendium of breaking news, emerging issues, and recent developments in the energy industry.
The Energy Industry Update – Volume 13, Issue 1
Energy Industry Update
The Energy Industry Update is a semi-annual publication features our view of recent significant events and emerging trends in the energy industry.

Gas-Power Interdependence
White Paper
This white paper examines the growing interdependence between the natural gas and electric industries.

Carbon Reduction Begins with Carbon Accounting
Article
Before setting any carbon reduction goals or developing a roadmap to achieve targets, organizations must first understand their emissions profile. Carbon accounting is the process of identifying…

The Continued Decline of Carbon-Free Generation in the United States and Implications for the Energy Future
Article
What are the implications of the potential loss of carbon-free generation? This article examines key issues and what it means for the energy future.

Spinning Our Wheels: How Nuclear Plant Closures Threaten to Offset Gains from Renewables
White Paper
This report explores how the progress created by solar and wind carbon-free generation is “at risk” of being reversed due to early retirement of currently operating nuclear…

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 16, Issue 2
Energy Industry Update
The energy industry is changing, and its regulatory and financial moorings are shifting. Competitive markets combined with other factors may lead to early nuclear unit retirement. Continuing…

One Step Forward, Two Steps Back… The Worsening Risk of Losing Carbon-Free Generation in the United States
White Paper
This report explores the shift in nuclear carbon-free generation in the U.S. and implications for our energy future.

Energy Industry Update – A Strategic Overview
Report
Energy Industry Update – A Strategic Overview
The Energy Industry Update – Volume 15, Issue 1
Energy Industry Update
The ScottMadden Energy Industry Update – Winter 2015 Changes: Turn and Face the Strange

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 14, Issue 1
Energy Industry Update
The ScottMadden Energy Industry Update – Winter 2013-2014 Here Comes the Sun and I Say...It’s Alright

Greening the Grid: An Overview of the Greening of the U.S. Generation Fleet
Report
Greening the Grid-a study of the trends and drivers impacting the United States electric grid and its movement towards renewable energy.

Clean Tech and Environment – Volume 17 – Issue 1
Report
In this section of the Energy Industry Update, we share lessons from Australia's experience with high levels of rooftop solar and differing approaches to structuring and pricing…

Infrastructure and Technology – Volume 16 – Issue 1
Report
This section of the Energy Industry Update reviews energy and utility companies and how they are accommodating larger penetration of renewable resources (including distributed PV) on their…

The Energy Industry Update – Volume 13, Issue 2
Energy Industry Update
The ScottMadden Energy Industry Update – Early Fall 2013 The Times They Are a-Changin’ (or Serenity Now!)

Facing Disruption Like We Have Never Experienced It Before
Article
We’ve talked for decades about disruption in the electric and gas industries. We’ve faced “unprecedented challenges,” existential threats, fundamental policy changes, exponential technology growth, extreme weather events,…

Build Your Own Texas: Tex Mix – The Generation Mix You Have vs. The Generation Mix You Could Have
Article
Episode 1: In response to Winter Storm Uri that hit Texas' electricity grid in February 2021, we built an interactive model to determine how the ERCOT grid…

Project Management Assessment for a T&D Utility
Case Study
A large transmission and distribution utility was seeking to improve the consistency of project cost and schedule for a capital project delivery to ensure it was eligible…
Transforming Your OT Function to Meet the Needs of the Changing Utility Industry
Article
Operational technology (OT) is a mission-critical function that must increasingly respond to industry changes. The traditional OT model distributed OT responsibilities across operating areas, embedding these responsibilities…

Power Decarbonization: Past and Future
White Paper
Decarbonization has become an increasingly important issue in the United States as more states, cities, and utilities commit to net-zero carbon-emissions goals. This report analyzes historical carbon…

Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act
Article
On November 15, 2021, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act or IIJA was passed. This act allows funds to be authorized to highways, highway safety programs, as…

Build Your Own Texas: Where (and When) the Wind Blows and the Sun Shines
Article
Episode 2: In this episode, the model uncovers challenges and capacity demand that regulators, utility executives, and customer advocacy groups should consider as coal phases out and…

Grid Modernization Cost-Benefit Framework and Tests
White Paper
Grid modernization efforts will play a critical role in today’s changing energy landscape. Demonstrating the value of grid modernization investments is necessary to gain regulatory approval of…

Racing to Net-Zero
Case Study
Our client, a mid-sized vertically integrated electric utility, announced one of the most aggressive net-zero carbon emissions goals in the United States. The company embarked on a…

Coming Clean: The Highs and Lows of the Clean Energy Transition
Pillar
Momentum toward a clean energy future seems certain. The difficulties related to the clean energy transition are evident as the industry implements these goals.
The Energy Industry Update – Volume 22, Issue 1
Energy Industry Update
This Energy Industry Update (EIU) examines how the combination of rising post-pandemic energy demand, ambitious decarbonization targets, high commodity prices, and geopolitical events are combining to put…

Wind Power Plant Acquisition
Case Study
To take advantage of an acquisition opportunity, our client, a power generation investment firm, contacted ScottMadden to support the diligence of an in development utility-scale wind energy…

Strategic Growth Plan for a Renewables Owner & Operator
Case Study
A national developer, owner, and operator of utility-scale wind, solar, and battery storage assets recently completed a major acquisition, expanding their asset portfolio and project pipeline to…

Five Keys to Successful IIJA and IRA Applications
Article
Through the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), also known as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), and the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), Congress has authorized nearly $400…

DOE Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) Grant Applications Support
Case Study
Our client, a large Midwest U.S. electric and gas utility, was interested in capitalizing on the significant funding opportunities presented by the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act…

Illinois Utilities Release Multi-Year Integrated Plans
Infographic
Distribution investment has been growing steadily for at least a decade and is expected to comprise the most significant portion of utility capital spending over the next…
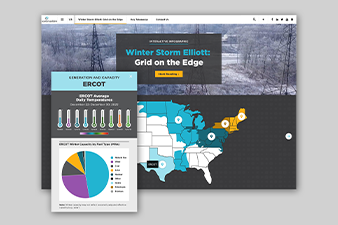
Winter Storm Elliott: Grid on the Edge
Infographic
A powerful cold front (or polar vortex) developed in the United States and Canada beginning December 21. After strengthening over the Northern Plains, it descended and covered…

Grid Reliability Is Changing Before Our Eyes
Article
As the electric power industry navigates passage through the most significant era of transition since its origin, key questions regarding reliability are emerging. Most importantly, can the…

Utility Evolution Brings About the (Re)Integration of System Planning Processes
Article
A Brief History of Utility Planning Prior to the 1990s, investor-owned utilities (IOUs) were largely vertically integrated, housing each utility function—generation, transmission, and distribution—under one roof. This…

